-
nanhai,foshan, CN 526200

The Ultimate Guide to Roll Form Design: Best Practices and Tooling Insights
# The Ultimate Guide to Roll Form Design: Best Practices and Tooling Insights
Roll form design is a critical aspect of modern metal fabrication, especially for industries like **ventilation duct manufacturing**, **door and gate production**, and **ventilation duct engineering contracting**. Whether you’re designing a **roll form machine** or optimizing **roll form tooling**, understanding the **key factors** that influence the **roll forming process** can significantly enhance your production efficiency and product quality. This article dives deep into the world of **roll form design**, offering a comprehensive **design guide** filled with **best practices**, **tooling insights**, and actionable tips to help you master the art of **roll forming**.
—
## Why This Article is Worth Reading
If you’re involved in **metal fabrication**, you know that **roll forming** is one of the most efficient methods for shaping **sheet metal** into complex profiles. However, the success of your **roll forming process** depends heavily on the **design of your roll form tooling** and the **roll form machine** you use. This article is packed with **design tips**, **case studies**, and **expert advice** to help you optimize your **roll form line**, reduce production costs, and improve product quality. Whether you’re a seasoned **roll form engineer** or new to the industry, this guide will provide valuable insights to elevate your **roll forming design** game.
—
## Article Outline
1. **What is Roll Forming and Why is it Important?**
2. **How Does the Roll Forming Process Work?**
3. **What Are the Key Factors in Roll Form Design?**
4. **What Role Does Tooling Play in Roll Forming?**
5. **How to Choose the Right Roll Form Machine for Your Needs?**
6. **What Are the Best Practices for Roll Form Tooling Design?**
7. **How to Optimize Strip Width and Material Thickness in Roll Forming?**
8. **What Are the Common Challenges in Roll Forming and How to Overcome Them?**
9. **Case Study: Successful Roll Forming in Ventilation Duct Manufacturing**
10. **FAQs About Roll Form Design and Tooling**
—
## 1. What is Roll Forming and Why is it Important?
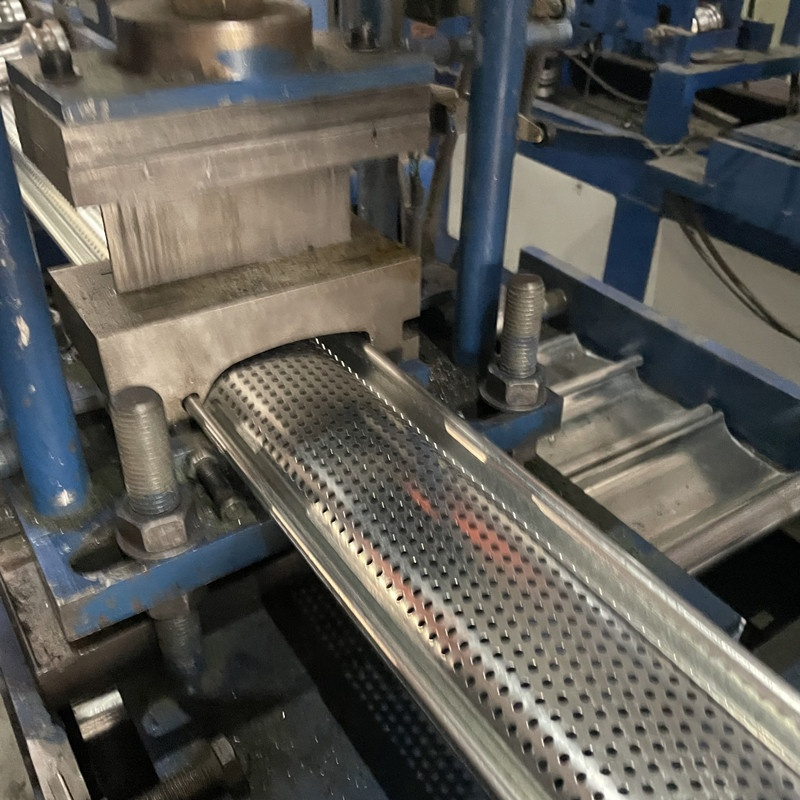
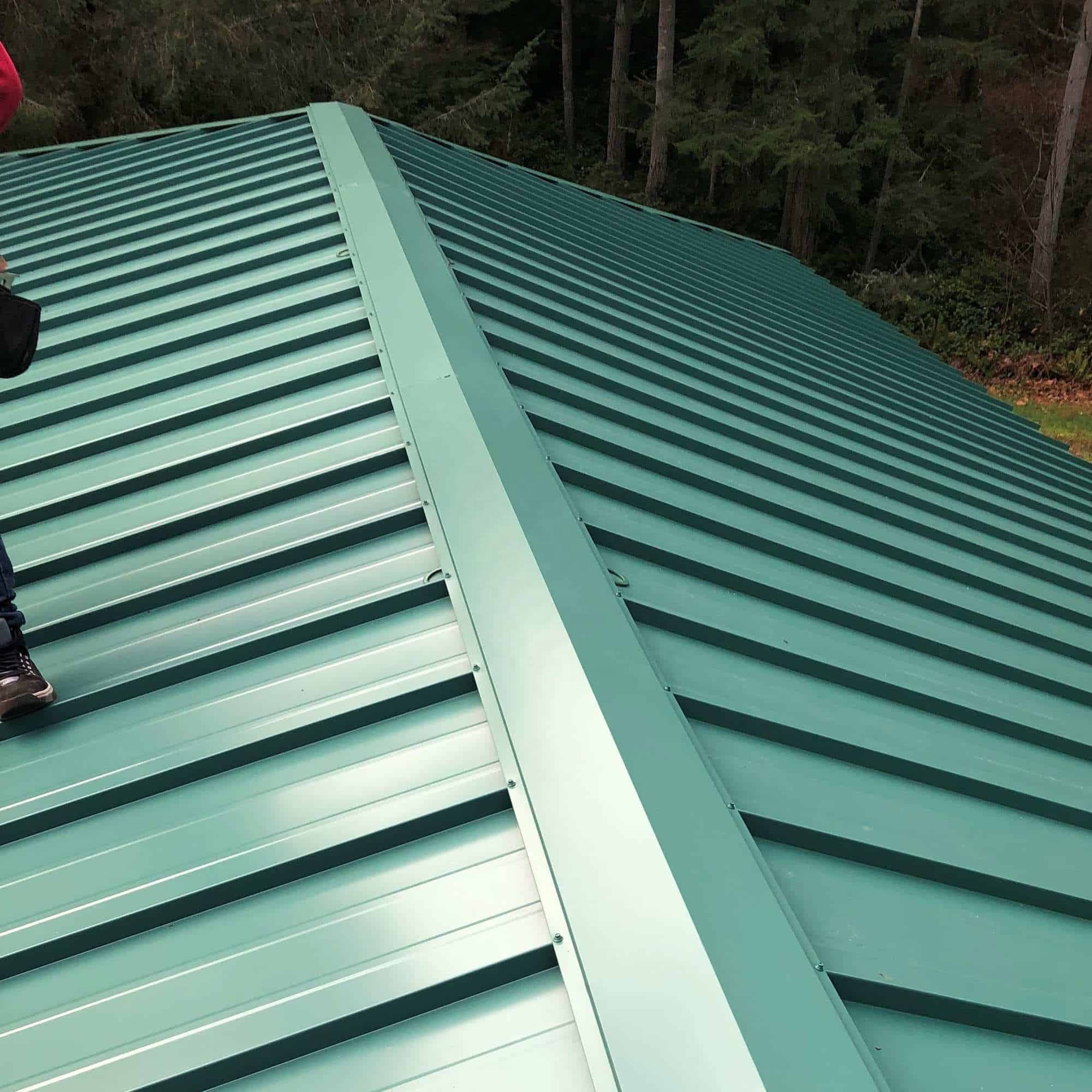
Roll forming is a continuous **metal fabrication** process that involves passing a **strip of metal** through a series of **forming rolls** to achieve a desired cross-sectional profile. This method is widely used in industries like **ventilation duct manufacturing** and **door and gate production** because it offers high precision, repeatability, and efficiency.
The importance of **roll forming** lies in its ability to produce complex shapes with minimal material waste. Unlike other **forming methods**, roll forming allows for the creation of long, continuous profiles, making it ideal for applications like **ventilation ducts** and **steel studs**. Additionally, the process can handle a wide range of materials, including **mild steel**, **aluminum**, and **galvanized steel**, making it versatile for various industries.
—
## 2. How Does the Roll Forming Process Work?
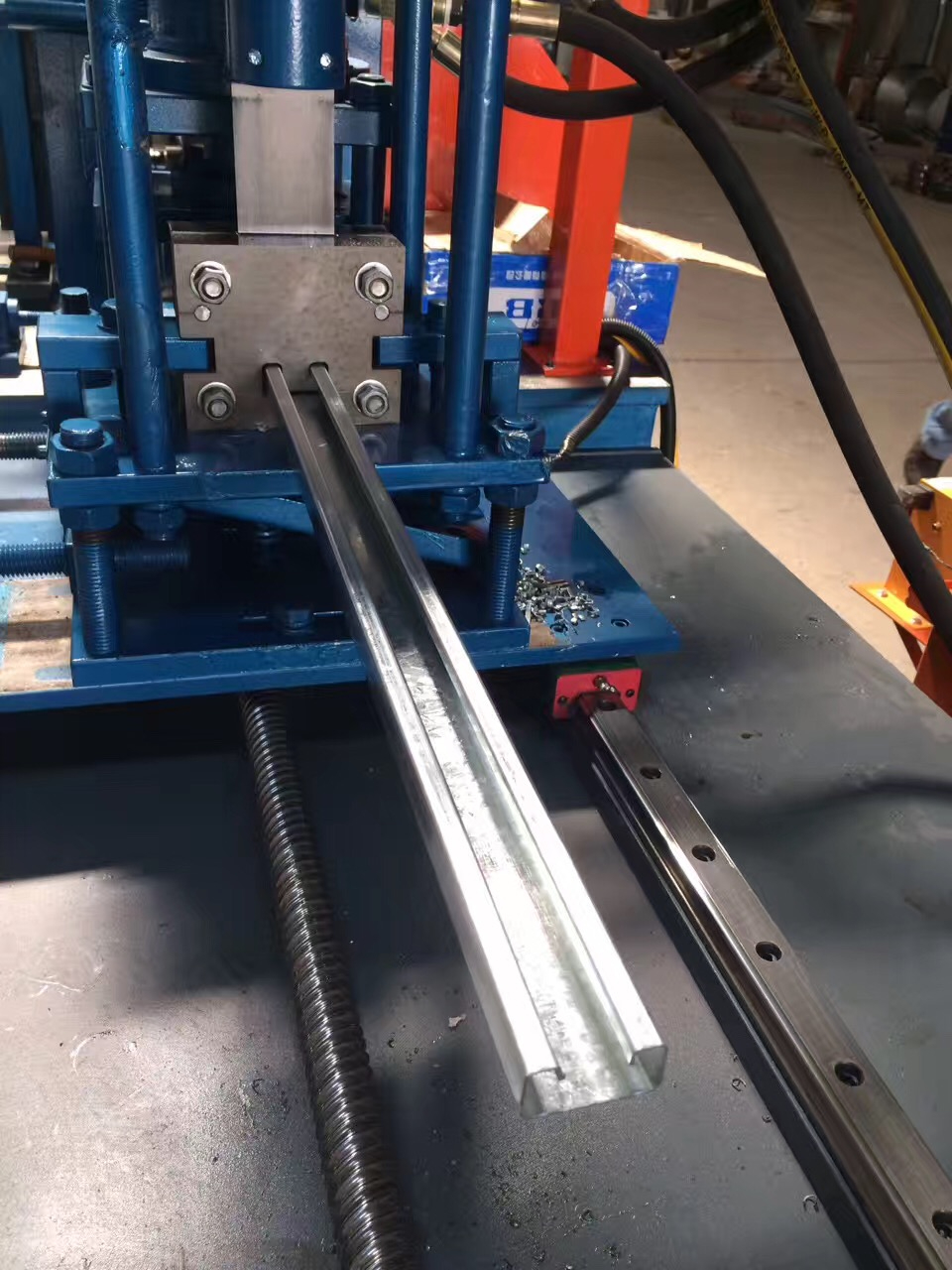
The **roll forming process** begins with a flat **sheet of metal** that is fed into a **roll form machine**. The machine consists of multiple **roll stations**, each equipped with a set of **forming rolls** that gradually shape the metal into the desired profile. As the metal passes through each station, it undergoes incremental **bends** until the final shape is achieved.
One of the key advantages of this process is its ability to handle high volumes of production with consistent quality. The **roll forming process** is also highly customizable, allowing manufacturers to adjust parameters like **strip width**, **material thickness**, and **bend radii** to meet specific requirements.
—
## 3. What Are the Key Factors in Roll Form Design?
When designing a **roll form line**, several **key factors** must be considered to ensure optimal performance:
– **Material Thickness**: The thickness of the **sheet metal** affects the amount of force required to form the material. Thicker materials may require more **roll pressure** and larger **roll diameters**.
– **Strip Width**: The width of the metal strip determines the size of the final profile and influences the **roll space** required in the machine.
– **Yield Strength**: The **yield strength** of the material impacts how much **forming** can be done in each pass. Materials with higher **yield strength** may require more passes to achieve the desired shape.
– **Bend Radii**: The radius of each **bend** affects the overall profile and must be carefully calculated to avoid defects like cracking or wrinkling.
By considering these factors during the **design phase**, you can create a **roll form line** that maximizes efficiency and minimizes production issues.
—
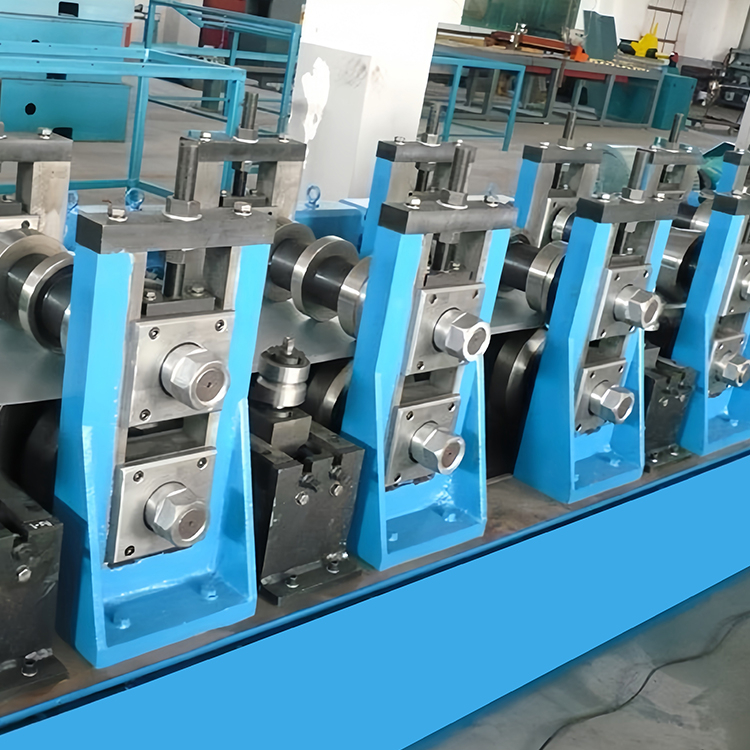
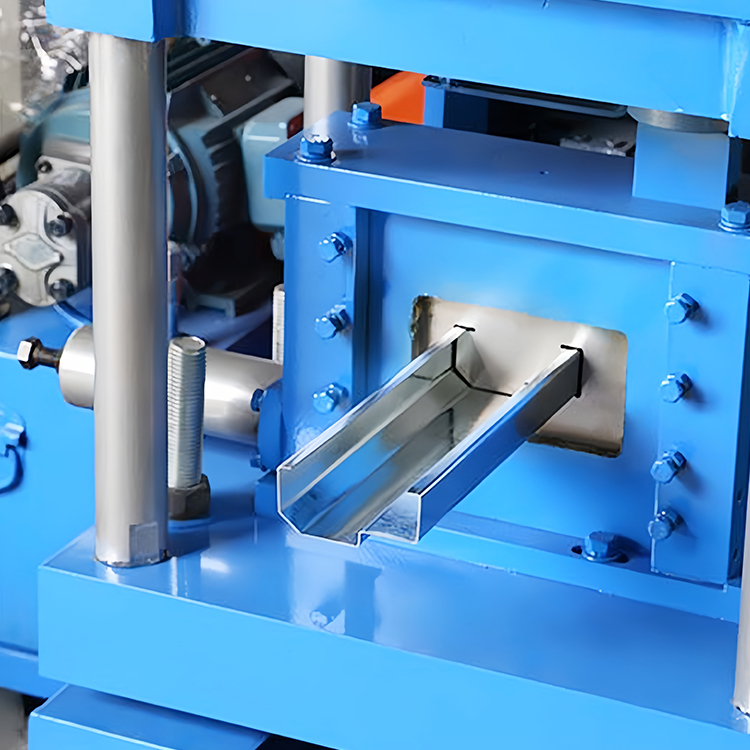
## 4. What Role Does Tooling Play in Roll Forming?
**Tooling** is the backbone of any **roll forming process**. The **roll form tooling** includes the **forming rolls**, **roll stands**, and other components that shape the metal. High-quality **tooling design** ensures that the metal is formed accurately and consistently, reducing the risk of defects and downtime.
One of the biggest challenges in **tooling design** is predicting how the metal will react during the **forming process**. Experienced **roll form engineers** use **computer-aided design (CAD)** software to simulate the **forming process** and optimize the **tooling** before production begins. This approach helps to identify potential issues early in the **design process**, saving time and resources.
—
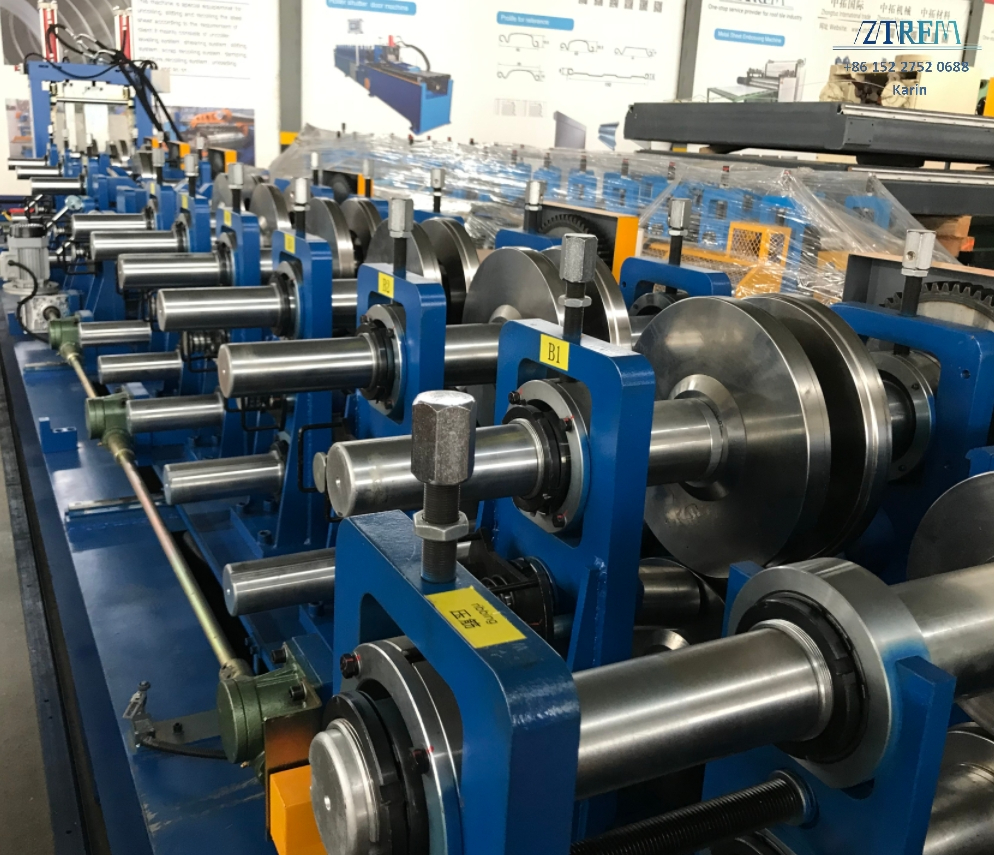
## 5. How to Choose the Right Roll Form Machine for Your Needs?
Choosing the right **roll form machine** is crucial for achieving optimal results in your **metal fabrication** projects. Here are some factors to consider:
– **Production Volume**: High-volume production may require a fully **automatic roll forming machine**, while smaller batches can be handled with semi-automatic or manual machines.
– **Material Type**: Different machines are designed to handle specific materials, such as **mild steel**, **aluminum**, or **galvanized steel**.
– **Profile Complexity**: Complex profiles may require machines with more **roll stations** and advanced **forming tooling**.
For example, if you’re manufacturing **ventilation ducts**, you might consider a machine like the **Automatic C&U Channel Steel Stud and Track Keel Roll Forming Machine**, which is designed for high precision and efficiency.
—
## 6. What Are the Best Practices for Roll Form Tooling Design?
Designing effective **roll form tooling** requires a combination of technical knowledge and practical experience. Here are some **best practices** to follow:
– **Use CAD Software**: **Computer-aided design** tools allow you to simulate the **forming process** and optimize the **tooling** before production.
– **Consider Material Properties**: The **yield strength** and **material thickness** of the metal will influence the **tooling design**.
– **Optimize Roll Diameters**: Larger **roll diameters** can handle thicker materials, but they may also increase the overall size of the machine.
By following these **best practices**, you can create **roll form tooling** that delivers consistent, high-quality results.
—
## 7. How to Optimize Strip Width and Material Thickness in Roll Forming?
Optimizing **strip width** and **material thickness** is essential for achieving the desired profile and minimizing waste. Here are some tips:
– **Calculate Strip Width**: The **strip width** should be calculated based on the final profile and the amount of **forming** required in each pass.
– **Adjust Material Thickness**: Thicker materials may require more passes and larger **roll diameters**, while thinner materials can be formed more quickly.
For example, when designing a **roll form line** for **galvanized steel** doors, you might need to adjust the **strip width** to accommodate the **bend radii** and ensure a smooth finish.
—
## 8. What Are the Common Challenges in Roll Forming and How to Overcome Them?
Despite its many advantages, **roll forming** can present several challenges, including:
– **Material Springback**: After **forming**, the metal may spring back slightly, altering the final profile. This can be mitigated by overforming the material slightly during the **forming process**.
– **Tooling Wear**: Over time, the **forming rolls** may wear down, leading to inconsistencies in the final product. Regular maintenance and timely replacement of **tooling** can help prevent this issue.
By understanding these challenges and implementing effective solutions, you can ensure a smooth and efficient **roll forming process**.
—
## 9. Case Study: Successful Roll Forming in Ventilation Duct Manufacturing
A leading **ventilation duct manufacturer** faced challenges with inconsistent profiles and high material waste. By partnering with a **roll form machine OEM**, they implemented a fully **automatic roll forming machine** with optimized **tooling design**. The result was a 30% reduction in material waste and a significant improvement in product consistency.
This case study highlights the importance of investing in high-quality **roll form machines** and **tooling** to achieve optimal results in **metal fabrication**.
—
## 10. FAQs About Roll Form Design and Tooling
**What is the difference between roll forming and other metal forming methods?**
Roll forming is a continuous process that uses a series of **forming rolls** to shape metal, while other methods like stamping or extrusion may involve single-step processes.
**How do I choose the right roll form machine for my needs?**
Consider factors like **production volume**, **material type**, and **profile complexity** when selecting a **roll form machine**.
**What are the key factors in roll form tooling design?**
Key factors include **material thickness**, **strip width**, **yield strength**, and **bend radii**.
**How can I optimize my roll forming process?**
Use **CAD software** to simulate the **forming process**, optimize **tooling design**, and regularly maintain your **roll form machine**.
**What are the common challenges in roll forming?**
Common challenges include **material springback** and **tooling wear**, which can be mitigated through proper **design** and maintenance.
**Can roll forming be used for different materials?**
Yes, roll forming can handle a variety of materials, including **mild steel**, **aluminum**, and **galvanized steel**.
—
## Summary of Key Points
– **Roll forming** is a highly efficient **metal fabrication** process used in industries like **ventilation duct manufacturing** and **door and gate production**.
– The success of the **roll forming process** depends on factors like **material thickness**, **strip width**, and **tooling design**.
– High-quality **roll form tooling** and **machines** are essential for achieving consistent, high-quality results.
– By following **best practices** and addressing common challenges, you can optimize your **roll forming process** and improve production efficiency.
—

For more information on **roll form machines** and **tooling design**, check out our [Metal Siding Roll Forming Machine](https://rollformingmachineoem.com/metal-siding-roll-forming-machine/) and [Fully Automatic Box Beam Roll Forming Machine](https://rollformingmachineoem.com/fully-automatic-box-beam-roll-forming-machine/).